Restaurant Glossary
Sales Per Labor Hour
Definition:
Sales Per Labor Hour is a key performance metric in the restaurant industry that measures the amount of revenue generated for every hour worked by an employee.
SPLH is calculated by dividing the total sales by the total labor hours worked during a specific period.
This metric is crucial for assessing labor efficiency, optimizing staffing levels, and controlling labor costs while ensuring that the restaurant maintains high service standards.
Why It Matters:
- Labor Efficiency:
SPLH provides insight into how efficiently a restaurant is using its labor force to generate revenue.A higher SPLH indicates that employees are contributing to more sales per hour worked, which is a sign of efficient labor management.
- Cost Control:
Labor is one of the largest expenses in the restaurant industry.By monitoring SPLH, operators can better control labor costs and ensure that staffing levels are aligned with sales performance.
This helps maintain profitability.
- Staffing Optimization:
Understanding SPLH allows restaurant managers to optimize staffing schedules by ensuring that the right number of employees are working during peak and off-peak hours.This balance helps maintain service quality while avoiding overstaffing or understaffing.
- Performance Benchmarking:
SPLH can be used to benchmark performance across different shifts, days, or locations.Comparing SPLH across these variables helps identify areas for improvement and best practices that can be applied more broadly.
Calculation:
SPLH is calculated using the following formula:
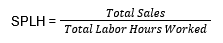
For example, if a restaurant generates $10,000 in sales during a shift where employees worked a combined total of 100 hours, the SPLH would be:
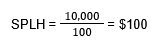
This means the restaurant generated $100 in sales for every labor hour worked during that shift.
Example in Action:
A popular casual dining restaurant notices that its SPLH is lower during weekday lunch shifts compared to weekend dinner shifts.
To address this, the manager reviews staffing levels and decides to reduce the number of staff during the slower weekday lunches, while maintaining full staffing during busy weekend dinners.
The restaurant also implements cross-training, enabling employees to handle multiple roles, which further improves efficiency.
As a result, the SPLH increases during weekday lunches, leading to better labor cost management and overall profitability.
Additional Resources & Related Terms
- Labor Cost Percentage:
The percentage of total sales that is spent on labor costs, often used alongside SPLH to assess labor efficiency.
- Revenue Per Available Seat Hour (RevPASH):
A related performance metric used in the restaurant industry to measure the revenue generated for each available seat during a specific hour of operation.
- Labor Law Compliance:
Labor Law Compliance in the restaurant industry refers to the adherence to federal, state, and local labor laws and regulations that govern employment practices.
Conclusion:
Sales Per Labor Hour (SPLH) is a vital metric for restaurants aiming to balance labor costs with sales performance.
By measuring the revenue generated per labor hour, restaurant operators can optimize staffing, control costs, and improve overall efficiency.
Regularly monitoring SPLH helps ensure that the restaurant is making the most of its labor resources, ultimately contributing to sustained profitability and operational success.