Restaurant Glossary
Employee Turnover Rate
Definition:
Employee Turnover Rate is a metric used in the restaurant industry to measure the percentage of employees who leave a restaurant over a specific period, typically a year.
This rate includes both voluntary departures, such as resignations, and involuntary ones, such as layoffs or terminations.
A high employee turnover rate can indicate issues such as poor job satisfaction, inadequate compensation, or a lack of career development opportunities.
Conversely, a low turnover rate suggests that employees are more likely to stay with the restaurant.
Additionally, this can lead to greater operational stability and lower recruitment and training costs.
Why It Matters:
- Cost Implications:High turnover rates can be costly for restaurants due to the expenses associated with recruiting, hiring, and training new employees.Frequent turnover disrupts operations and increases labor costs, affecting the restaurant’s bottom line.
- Operational Stability:Consistent turnover can lead to a lack of experienced staff, which can negatively impact service quality, customer satisfaction, and overall efficiency.Maintaining a lower turnover rate helps ensure that the restaurant has a skilled and knowledgeable team.
- Workplace Culture:A high turnover rate can harm workplace culture, leading to low morale, decreased employee engagement, and a fragmented team.On the other hand, a stable workforce contributes to a positive work environment, which further enhances retention.
- Customer Experience:Regular customers often appreciate familiar faces and consistent service. High employee turnover can disrupt this continuity, potentially leading to a decline in customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Calculation:
Employee Turnover Rate is typically calculated by dividing the number of employees who leave during a specific period by the average number of employees during that period, then multiplying by 100 to get a percentage.
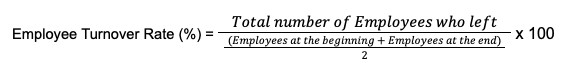
For example, if a restaurant had 20 employees at the start of the year, hired 10 more throughout the year, and 15 employees left, the turnover rate would be:

Example in Action:
A restaurant experiences an employee turnover rate of 70% over the past year, significantly above the industry average.
To address this, the management conducts exit interviews to understand the reasons for staff departures and identifies key issues such as low wages and lack of career progression.
In response, the restaurant implements a competitive pay structure, introduces clear career advancement opportunities, and enhances its training programs.
Over the next year, the turnover rate drops to 40%, leading to improved operational stability and higher customer satisfaction.
Additional Resources & Related Terms
- Employee Engagement:
Employee Engagement in the restaurant industry refers to the emotional commitment and level of enthusiasm that employees have towards their work, their team, and the restaurant they work for.
Creating an inclusive work environment enhances employee engagement by making all employees feel valued and included. - Gen Zs Flooding into Workforce as Boomers Exit—How Can Restaurants Manage This Shift?:To secure their share of new talent and overcome persisting staffing challenges, restaurants may have to rethink their approaches.Additionally, the social cause most likely to motivate Gen Z to join a company is supporting diversity, equity, and inclusion.
Read more about how a brand can attract, manage, and retain a younger workforce.
- Job Satisfaction:
The level of contentment and fulfillment employees feel about their work in a restaurant setting.
Conclusion:
Employee Turnover Rate is a critical metric for restaurants to monitor, as it directly affects operational efficiency, costs, and workplace culture.
By understanding and addressing the factors that contribute to high turnover, restaurants can implement strategies to reduce turnover rates, improve employee retention, and create a more stable and productive work environment.
This not only benefits the employees but also enhances the overall customer experience and contributes to the long-term success of the restaurant.