Restaurant Glossary
Net Profit Margin
Definition:
Net Profit Margin is a key financial metric in the restaurant industry that measures the percentage of revenue remaining after all expenses have been deducted.
This includes the cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, taxes, and interest.
Therefore, it is a clear indicator of a restaurant’s profitability, showing how much of each dollar of revenue is retained as profit.
This metric is calculated by dividing the net profit by total revenue and multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage.
Why It Matters:
- Profitability Indicator:
Net profit margin provides a direct measure of a restaurant’s financial health.
A higher margin indicates that the restaurant is efficiently managing its costs and generating more profit from its sales. - Financial Planning:
Understanding your margin helps restaurant owners and managers make informed decisions about pricing, cost management, and investment strategies.
Thus, it allows for better financial planning and goal setting. - Benchmarking:Understanding your margin allows restaurants to compare their profitability against industry standards or competitors, helping identify areas for improvement and opportunities for growth.
- Sustainability:
Maintaining a healthy net profit margin is crucial for the long-term sustainability of a restaurant.
Therefore, it ensures that the business can cover its costs, invest in improvements, and withstand economic fluctuations.
Calculation:
Net Profit Margin is calculated using the following formula:
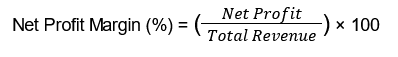
Where:
- Net Profit is the total revenue minus all expenses, including COGS, operating expenses, taxes, and interest.
- Total Revenue is the total income generated from sales.
For example, if a restaurant has a total revenue of $200,000 and net profits of $20,000, the net profit margin would be:
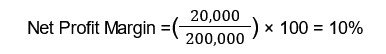
This means that 10% of the restaurant’s revenue is retained as profit after all expenses are paid.
Example in Action:
A mid-sized restaurant analyzes its net profit margin and finds it is consistently around 8%, slightly below the industry average.
To improve this, the management decides to focus on reducing food waste, negotiating better deals with suppliers, and optimizing staff scheduling to lower labor costs. Additionally, they increase the price of a few high-demand menu items with minimal impact on customer traffic.
Therefore, over the next quarter, these changes result in an improvement of 12%, reflecting more efficient operations and better cost management.
Additional Resources & Related Terms
- Gross Profit Margin:The percentage of revenue remaining after subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS), before other operating expenses are deducted.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS):The direct costs of producing the food and beverages sold by the restaurant, a key factor in calculating both gross and net profit margins.
Conclusion:
Net Profit Margin is a crucial metric for assessing the overall profitability and financial health of a restaurant.
By regularly monitoring and optimizing this percentage, restaurant operators can make strategic decisions that enhance profitability, improve operational efficiency, and ensure the long-term success of their business.
Thus, understanding and managing your margin is essential for achieving sustainable growth in the competitive restaurant industry.