Restaurant Glossary
Inventory Turnover Ratio
Definition:
The Inventory Turnover Ratio is a financial metric used in the restaurant industry to measure how often a restaurant’s inventory is sold and replaced over a specific period, usually a month or year.
It is calculated by dividing the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) by the average inventory value during the same period.
So, a higher inventory turnover ratio indicates that inventory is being used efficiently and is quickly converted into sales. Meanwhile, a lower ratio may suggest overstocking, inefficiencies, or slow-moving inventory.
Why It Matters:
- Operational Efficiency:
It provides insight into how efficiently a restaurant is managing its inventory.
Also, a high ratio suggests that the restaurant is effectively utilizing its resources, minimizing waste, and ensuring that ingredients are fresh. - Cost Control:
Monitoring the inventory turnover ratio helps restaurants identify and reduce waste from slow-moving or excess inventory.In other words, this leads to better cost management and increased profitability.
- Cash Flow Management:
A healthy ratio ensures that capital is not tied up in excess inventory, improving cash flow and allowing the restaurant to invest in other operational areas.
- Quality and Freshness:
Frequent inventory turnover ensures that ingredients are fresh. This is crucial for maintaining high food quality and customer satisfaction.
Calculation:
The Inventory Turnover Ratio is calculated using the following formula:
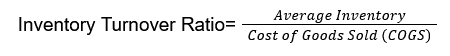
Where:
- COGS is the total cost of the ingredients and items used to produce the food sold during the period.
- Average Inventory is the average value of inventory over the same period, calculated as:

For example, let’s say a restaurant has a COGS of $50,000. And then say they have an average inventory value of $10,000 for the month. The inventory turnover ratio would be:

This means the restaurant’s inventory turns over five times during the month.
Example in Action:
A popular restaurant notices that its inventory turnover ratio has decreased to 2 times per month. It’s indicating that inventory is sitting too long before being used.
After investigating, the management discovers that certain ingredients, like exotic spices and specialty meats, are over-ordered.
Therefore, they then notice that it’s not being used quickly enough, leading to waste.
So, the restaurant adjusts its ordering practices to better align with actual usage and focuses on using these ingredients in daily specials.
Thus this improves the inventory turnover ratio to 4 times per month, reducing waste and freeing up cash flow for other needs.
Additional Resources & Related Terms
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS):
The direct costs associated with producing the food and beverages sold by a restaurant, including ingredients and related supplies.
- Gross Profit Margin:
A financial metric that measures the proportion of revenue remaining after accounting for the cost of goods sold (COGS), which includes the direct costs associated with producing the food and beverages sold by a restaurant.
- Food Cost Percentage:
A key performance indicator that shows the ratio of food costs to total food sales, used to measure and control the cost efficiency of a restaurant’s menu.
Conclusion:
The Inventory Turnover Ratio is a crucial metric for restaurants to monitor, as it directly impacts cost control, cash flow, and the quality of the food served.
By regularly analyzing and optimizing this ratio, restaurant operators can reduce waste, improve efficiency, and ensure that their inventory management practices align with their financial and operational goals.
Therefore, understanding and managing this ratio is key to maintaining a successful and profitable restaurant.