Restaurant Glossary
Customer Turnover Rate
Definition:
Customer Turnover Rate, also known as table turnover rate, is a metric used in the restaurant industry to measure the average number of times a table is occupied by different customers during a specific period, usually an hour or a shift.
This rate is an important indicator of a restaurant’s efficiency in serving customers and maximizing seating capacity.
A higher turnover typically correlates with increased revenue, as it indicates that more customers are being served in a given time frame.
Why It Matters:
- Revenue Maximization:
A higher table turnover rate allows a restaurant to serve more customers, leading to increased sales and revenue. Efficiently managing turnover can significantly impact the profitability of a restaurant, especially during peak hours.
- Operational Efficiency:
Monitoring the your Turnover Rate helps restaurants identify opportunities to streamline operations, such as reducing wait times, optimizing table seating, and improving kitchen efficiency. Faster turnover can enhance overall customer satisfaction by minimizing wait times for tables.
- Customer Experience:
While a high turnover rate is generally desirable, it’s important to balance speed with customer experience. Rushing customers can lead to dissatisfaction, while a well-managed turnover rate ensures a pleasant dining experience without unnecessary delays.
- Capacity Management:
Understanding turnover rates helps restaurant managers better forecast and manage seating capacity, staffing needs, and inventory levels. It also assists in planning for peak periods and optimizing the layout for maximum efficiency.
Calculation:
Customer Turnover Rate is typically calculated by dividing the total number of parties served by the number of tables available, over a specified period of time.
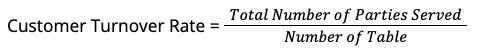
For example, if a restaurant with 20 tables serves 60 parties during a 3-hour dinner service, the table turnover rate would be:
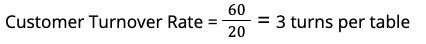
Example in Action:
A busy downtown bistro notices that its Customer Turnover Rate is lower than expected during lunch hours.
After analyzing the situation, management implements a more efficient ordering process and trains the staff to expedite service without compromising on quality.
These changes result in a higher turnover rate, allowing the bistro to serve more customers and increase revenue during the lunch rush.
Additional Resources & Related Terms
- Average Check:
The average amount spent per customer, which combined with a high turnover rate, can significantly impact overall revenue.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
In the restaurant industry, restaurants use strategies, tools, and technologies to manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV):
A key metric used to estimate the total revenue a restaurant can expect to earn from a customer over the duration of their relationship with the business.
Conclusion:
Customer Turnover Rate is a critical metric for restaurants aiming to maximize revenue and optimize operations.
By effectively managing turnover, restaurants can increase the number of customers served, enhance operational efficiency, and improve overall customer satisfaction, leading to greater profitability and long-term success.