Restaurant Glossary
Sales Index
Definition:
A Sales Index is a metric used in the restaurant industry to measure and compare sales performance across different periods, locations, or categories.
It is typically expressed as a percentage and is calculated by comparing actual sales to a baseline or target sales figure, such as sales from the same period in the previous year (Year-over-Year, or YoY).
The Index helps restaurant operators understand trends, identify growth opportunities, and assess the effectiveness of marketing and operational strategies.
Why It Matters:
- Performance Evaluation:
The Sales Index provides a clear view of how well a restaurant is performing compared to previous periods or against set targets. Therefore, it helps identify whether sales are increasing, decreasing, or remaining stable, offering insights into the restaurant’s overall health.
- Trend Analysis:
By analyzing the data over time, restaurant operators can identify trends.
Some trends include customer behavior, seasonal patterns, and the impact of promotions.
In other words, this information is valuable for planning future strategies and making informed decisions. - Benchmarking:
The Sales Index allows restaurants to benchmark their performance against industry standards or competitor locations. This helps operators understand where they stand in the market and identify areas for improvement.
- Strategic Decision-Making:
A positive or negative, a shift can guide strategic decisions such as menu adjustments, marketing initiatives, and staffing changes. Thus, it helps operators respond proactively to changes in the business environment.
Key Components of Sales Index:
- Baseline Sales:
The reference point or benchmark used to calculate the Sales Index. Therefore, this could be sales from a previous period, a target sales figure, or an average sales figure.
- Actual Sales:
The sales figure for the period being analyzed. This is compared to the baseline to determine the Sales Index.
- Calculation:
The Sales Index is calculated by dividing the actual sales by the baseline sales and multiplying by 100 to express the result as a percentage.
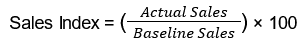
For example, if a restaurant had sales of $120,000 in June this year, compared to $100,000 in June last year, the Sales Index would be:
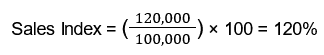
This indicates a 20% increase in sales compared to the previous year.
Example in Action:
A national pizza chain uses the Index to compare the performance of its locations across different regions.
The baseline sales figure is set as the average monthly sales from the previous year.
The chain notices that its Midwest locations have a Sales Index of 95%, indicating a slight decline in sales, while its West Coast locations have a Index of 110%, showing strong growth.
The management team investigates the reasons behind these trends and decides to increase marketing efforts in the Midwest while introducing new promotions on the West Coast to capitalize on the positive momentum.
Additional Resources & Related Terms
- Comp Sales
A key financial metric used in the restaurant industry to measure the performance of locations that have been open for a significant period, typically at least one year. - Dine in Sales
The total revenue generated from customers who physically dine at a restaurant’s location, as opposed to takeout, delivery, or drive-thru orders. - Food Cost Percentage
A key financial metric in the restaurant industry that measures the cost of ingredients used to prepare food relative to the revenue generated from selling those food items.
Conclusion:
The Sales Index is a powerful tool for measuring and analyzing a restaurant’s sales performance over time.
By comparing actual sales to a baseline, restaurant operators can gain insights into trends, evaluate the success of their strategies, and make informed decisions to drive growth.
So, regularly monitoring the Sales Index helps ensure that the restaurant remains competitive and responsive to changes in the market, ultimately contributing to long-term success.